Обработка форм сайта с помощью php
Содержание:
Атрибуты и свойства тега
1. Атрибут accept-charset=»Кодировка» — определяет кодировку, в которой сервер может принимать и обрабатывать данные формы. Может принимать различные значения, например, CP1251, UTF-8 и т.п.
2. Атрибут action=»URL» — адрес скрипта, который обрабатывает передаваемые данные от формы. Если оставить это значение пустым, то данные будут обрабатываться в этом же документе, где расположена форма.
3. Атрибут autocomplete=»on/off» — задает или отключает автозаполнение формы. Может принимать два значения:
- on — включить автозаполнение;
- off — выключить автозаполнение;
4. Атрибут enctype=»параметр» — задает способ кодирования данных. Может принимать следующие значения:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded — вместо пробелов ставится +, символы вроде русских букв кодируются их шестнадцатеричными значениями
- multipart/form-data — данные не кодируются
- text/plain — пробелы заменяются знаком +, буквы и другие символы не кодируются.
5. Атрибут method=»POST/GET» — задает метод отправки. Может принимать два значения:
- GET — передача данных в адресной строке (есть ограничение по объёму отправки данных)
- POST — посылает на сервер данные в запросе браузера (может отправить большое количество данных, т.к. нету ограничения объёма)
Более подробное описание методов передачи через GET и POST читайте в уроках по PHP: использование методов GET и POST.
6. Атрибут name=»имя» — задает имя формы. Чаще всего используется в случае наличия множества форм для того, чтобы можно было обратиться к конкретной форме через скрипт.
7. Атрибут novalidate — отменяет встроенную проверку данных формы на корректность ввода.
8. Атрибут target=»параметр» — имя окна или фрейма, куда обработчик будет загружать возвращаемый результат. Может принимать следующие значения:
- _blank — загружает страницу в новое окно браузера
- _self — загружает страницу в текущее окно
- _parent — загружает страницу во фрейм-родитель
- _top — отменяет все фреймы и загружает страницу в полном окне браузера
Уважаемый читатель, теперь Вы узнали гораздо больше о html теге form. Теперь советую перейти к следующему уроку.
Ссылка на следующий урок: Урок 9. HTML тег div — подробное описание с примерами
List of All Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| accept-charset | Specifies the character encodings used for form submission |
| action | Specifies where to send the form-data when a form is submitted |
| autocomplete | Specifies whether a form should have autocomplete on or off |
| enctype | Specifies how the form-data should be encoded when submitting it to the server (only for method=»post») |
| method | Specifies the HTTP method to use when sending form-data |
| name | Specifies the name of the form |
| novalidate | Specifies that the form should not be validated when submitted |
| rel | Specifies the relationship between a linked resource and the current document |
| target | Specifies where to display the response that is received after submitting the form |
❮ Previous
Next ❯
HTML Exercises
List of All <form> Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| accept-charset | Specifies the character encodings used for form submission |
| action | Specifies where to send the form-data when a form is submitted |
| autocomplete | Specifies whether a form should have autocomplete on or off |
| enctype | Specifies how the form-data should be encoded when submitting it to the server (only for method=»post») |
| method | Specifies the HTTP method to use when sending form-data |
| name | Specifies the name of the form |
| novalidate | Specifies that the form should not be validated when submitted |
| rel | Specifies the relationship between a linked resource and the current document |
| target | Specifies where to display the response that is received after submitting the form |
❮ Previous
Next ❯
HTML Tutorial
HTML HOMEHTML IntroductionHTML EditorsHTML BasicHTML ElementsHTML AttributesHTML HeadingsHTML ParagraphsHTML StylesHTML FormattingHTML QuotationsHTML CommentsHTML Colors
Colors
RGB
HEX
HSL
HTML CSSHTML Links
Links
Link Colors
Link Bookmarks
HTML Images
Images
Image Map
Background Images
The Picture Element
HTML TablesHTML Lists
Lists
Unordered Lists
Ordered Lists
Other Lists
HTML Block & InlineHTML ClassesHTML IdHTML IframesHTML JavaScriptHTML File PathsHTML HeadHTML LayoutHTML ResponsiveHTML ComputercodeHTML SemanticsHTML Style GuideHTML EntitiesHTML SymbolsHTML EmojisHTML CharsetHTML URL EncodeHTML vs. XHTML
The Method Attribute
The attribute specifies the HTTP
method to be used when submitting the form data.
The form-data can be sent as URL variables (with )
or as HTTP post transaction (with ).
The default HTTP method when submitting form data is GET.
Example
This example uses the GET method when submitting the form data:
<form action=»/action_page.php» method=»get»>
Example
This example uses the POST method when submitting the form data:
<form action=»/action_page.php» method=»post»>
Notes on GET:
- Appends the form data to the URL, in name/value pairs
- NEVER use GET to send sensitive data! (the submitted form data is visible in the URL!)
- The length of a URL is limited (2048 characters)
- Useful for form submissions where a user wants to bookmark the result
- GET is good for non-secure data, like query strings in Google
Notes on POST:
- Appends the form data inside the body of the HTTP request (the submitted
form data is not shown in the URL) - POST has no size limitations, and can be used to send large amounts of data.
- Form submissions with POST cannot be bookmarked
Tip: Always use POST if the form data contains sensitive or personal information!
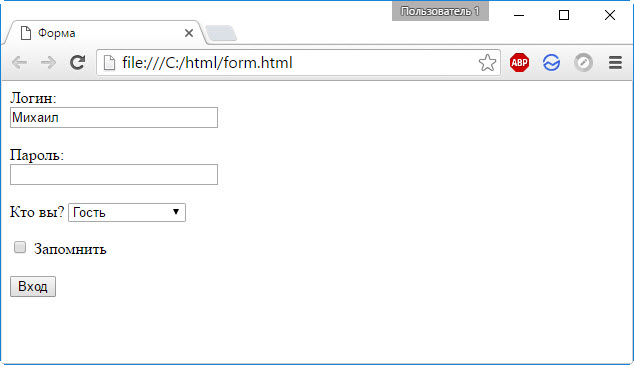
Пример 1. Форма html с кнопками
Преобразуется на странице в следующее:
Пояснения к примеру
- action=»» — говорит о том, что обработка данных будет происходить на этой же странице.
- <input type=»radio» name=»answer» value=»»> — атрибут type=»radio» говорит о том, что нужно отобразить текст после этого кода, как кнопку выбора. Атрибут name и value в данном теге для нас сейчас играют маленькую роль, т.к. мы не изучаем сейчас php (см. уроки php).
- <input type=»text» name=»poletext» value=»»> — атрибут type=»text» говорит о том, что это будет текстовое поле. Здесь так же есть два важных атрибута: name (для php) и value (значение по умолчанию).
- <input type=»textarea» name=»opisanie» value=»»> — атрибут type=»textarea» говорит о том, что это будет большое текстовое поле. Разница от предыдущего случая лишь в том, что он позволяет записывать большой объем текста.
- <input type=»submit» value=»»> — атрибут type=»submit» говорит о том, что это кнопка. В атрибуте value пишется то, что будет написано на кнопке.
Более подробно про все эти элементы можно прочитать в 15 уроке: элементы тега <form>, где рассмотрены радиокнопки, списки, флажки, текстовые поля, кнопки.
Теперь рассмотрим подробно все атрибуты тега <form>.
The Action Attribute
The attribute defines the action to be performed when the form is submitted.
Usually, the form data is sent to a file on the server when the user clicks on the submit button.
In the example below, the form data is sent to a file called «action_page.php».
This file contains a server-side script that handles the form data:
Example
On submit, send form data to «action_page.php»:
<form action=»/action_page.php»> <label for=»fname»>First
name:</label><br> <input type=»text» id=»fname» name=»fname»
value=»John»><br> <label for=»lname»>Last name:</label><br>
<input type=»text» id=»lname» name=»lname» value=»Doe»><br><br>
<input type=»submit» value=»Submit»></form>
Tip: If the attribute is omitted, the action is set to the current page.